Joseph Marie Jacquard in 1800 invented the loom also known as Jaquard’s Loom is a device to weave cloth with a certain amount of pressure. This simplified the process of manufacturing textiles with complex patterns. The loom is controlled by punched cards with punched holes, each row of which corresponds to one row of the design. Multiple rows of holes are punched on each card and the many cards that compose the design of the textile are strung together in order.
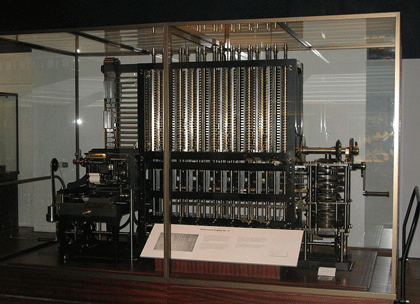
The Jacquard loom was the first machine to use punched cards to control a sequence of operations. Although it did no computation based on them, it is considered an important step in the history of computing hardware. The ability to change the pattern of the loom’s weave by simply changing cards was an important conceptual precursor to the development of computer programming. Specifically, Charles Babbage planned to use cards to store programs in his Analytical engine.